Geopolitics and Arctic Shipping Lanes: NATO, China, Russia
NATO addresses Arctic security by managing geopolitical tensions, protecting trade routes, and mitigating environmental risks as melting ice opens new shipping lanes. Learn about its military exercises, surveillance efforts, and collaboration to ensure stability in this strategically vital region.

The Arctic region is rapidly becoming a focal point in global geopolitics due to shifting dynamics. Newly accessible shipping lanes, such as the Northern Sea Route and the Northwest Passage, are significantly shortening travel times between Europe, Asia, and North America. For example, the Northern Sea Route can reduce the journey from Europe to Asia by about 40%, saving up to 10-15 days compared to traditional routes through the Suez Canal. While these routes offer strategic benefits, such as faster trade and improved resource access, they also present geopolitical challenges, including territorial disputes and the need for enhanced maritime security.
Countries like Russia, the United States, and China are increasingly competing for influence in the Arctic, each pursuing a range of strategic goals—from military dominance to securing critical trade routes and natural resources. Russia has strengthened its military presence with advanced bases and icebreaker fleets, the U.S. focuses on maintaining freedom of navigation and building alliances with Arctic nations, while China has invested heavily in Arctic infrastructure and scientific research under its Polar Silk Road initiative.
These actions reflect the diverse strategies shaping the Arctic's future, making control of these shipping lanes a crucial issue for global stability.
NATO’s Expanding Role in the Arctic
Why NATO is Involved
Historically, NATO’s presence in the Arctic has been limited. However, as the region becomes more accessible, the alliance has recognized the need to adapt to shifting geopolitical dynamics. Member states like Canada, Norway, and the United States have direct stakes in Arctic security, making it a priority for NATO to ensure stability and protect shared interests.
NATO’s involvement is driven by several factors:
Geopolitical Rivalries
The Arctic has become a focal point for global competition. Russia has established military bases in regions like Franz Josef Land and the Kola Peninsula, deployed advanced missile systems like the S-400, and increased its fleet of nuclear-powered icebreakers. These actions are part of Russia's strategy to secure northern territories and control key maritime routes. In response, NATO has increased its joint exercises and surveillance activities, framing them as defensive measures to ensure stability and deter aggression. For example, the deployment of maritime patrol aircraft, such as the P-8 Poseidon, enhances NATO's ability to monitor Arctic waterways and respond to emerging threats. Non-NATO Arctic nations, including Finland, Sweden, and Iceland, also play crucial roles, promoting sustainable development and regional stability through multilateral forums like the Arctic Council.
Economic Interests
Securing trade routes and ensuring the free flow of goods is vital for global commerce. The Northern Sea Route, for instance, offers significant reductions in travel time between Europe and Asia, providing competitive advantages for shipping companies and nations with access to these routes.
Key Actions Taken by NATO
NATO has ramped up its efforts to address Arctic security challenges through various initiatives:
Increased Military Exercises: NATO conducts regular joint exercises in the High North, such as “Cold Response” and “Dynamic Mongoose,” to enhance readiness and interoperability among member states. These exercises involve large-scale cold-weather training, coordination of Arctic-adapted weaponry, and testing of naval strategies under extreme conditions. Recent exercises have demonstrated improved joint operational capabilities and have strengthened the alliance’s ability to safeguard critical Arctic routes. These exercises include the testing of Arctic-adapted weaponry, deployment of amphibious forces, and coordination with advanced platforms like the F-35 fighter jets and Aegis-equipped naval ships to simulate defending shipping lanes and countering incursions.
Diplomatic Engagements: NATO has also pursued diplomatic and cooperative measures, such as participating in Arctic Council discussions and fostering dialogue with other regional stakeholders, to complement its military initiatives. NATO conducts regular joint exercises in the High North, such as “Cold Response” and “Dynamic Mongoose,” to enhance readiness and interoperability among member states. These exercises involve cold-weather combat training, the use of Arctic-adapted weapon systems, and joint naval operations to secure key shipping lanes and deter incursions from adversaries.
Enhanced Surveillance: The alliance has bolstered its Arctic surveillance with technologies like the Sentinel satellite network and high-altitude unmanned drones. Additionally, NATO has increased the deployment of maritime patrol aircraft like the P-8 Poseidon to monitor shipping lanes and track potential threats in real time.
Collaboration with Allies: NATO works closely with Arctic Council members and other regional stakeholders to promote cooperation and share intelligence on emerging risks. Additionally, Arctic Council initiatives, such as the Agreement on Enhancing International Arctic Scientific Cooperation, provide a platform for dialogue between NATO and non-NATO nations to address shared challenges.
Emerging Threats in the Arctic
Geopolitical Tensions
One of the most significant challenges in securing Arctic shipping lanes is the intensifying geopolitical rivalry, particularly between NATO and Russia. Russia has heavily invested in bolstering its military presence in the Arctic, establishing strategic bases like Nagurskoye on Franz Josef Land, expanding its fleet of nuclear-powered icebreakers, and deploying advanced defense systems such as the S-400 missiles. These measures are designed to assert Russia’s control over the region and ensure the security of its energy and trade routes.
In parallel, China’s growing interest in the Arctic is linked to its broader "Polar Silk Road" initiative, which is part of its expansive Belt and Road strategy. While China does not claim territory in the region, it has focused on developing economic ties through investments in Arctic infrastructure, energy projects, and scientific research. Notably, China has partnered with Russia on natural gas development on the Yamal Peninsula, reflecting its strategy to secure energy supplies and increase its influence in Arctic governance, thereby challenging NATO’s influence in the region.
Cybersecurity Concerns
As Arctic shipping lanes grow in importance, they are becoming targets for cyberattacks. Cyber incidents, including GPS jamming, have disrupted navigation systems. In response, NATO has developed advanced electronic warfare capabilities and increased cooperation among member states to protect critical infrastructure and ensure the security of Arctic shipping routes.
Recent incidents in the Baltic region have heightened concerns over cybersecurity and the protection of critical infrastructure. Notably:
- Undersea Cable Damage: On November 18, 2024, two undersea fiber-optic cables in the Baltic Sea were severed, disrupting internet connectivity between Finland and Germany, and between Lithuania and Sweden. German Defense Minister Boris Pistorius described the damage as a "clear act of sabotage," and Finnish authorities launched an investigation into the incident.
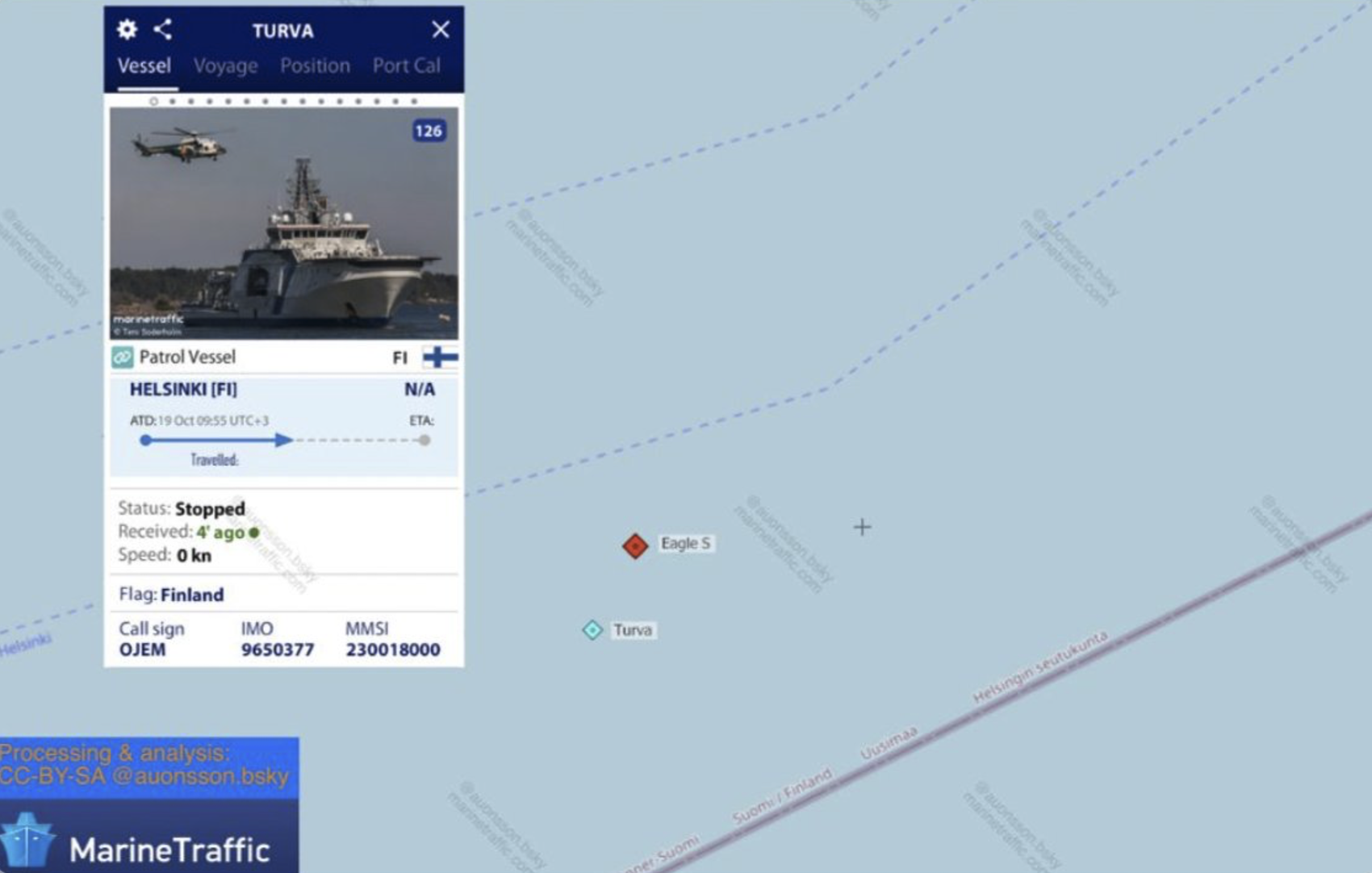
- Oil Tanker Detention: On December 25, 2024, Finnish authorities detained the Russian-linked oil tanker Eagle Sin connection with the damage to the Estlink 2 subsea electricity cable in the Baltic Sea. This cable, crucial for electricity transmission between Finland and the Baltics, was damaged on Christmas Day, and the Eagle S was observed near the cable at the time of the incident.
These events underscore the vulnerabilities of critical infrastructure in the Baltic region to cyber and hybrid warfare tactics. In response, NATO has been enhancing its cybersecurity measures, including the development of advanced electronic warfare capabilities and increased cooperation among member states to protect critical infrastructure and ensure the security of maritime routes.
For related stories on cybersecurity incidents in the Baltics and beyond:
Looking Ahead: NATO’s Future in Arctic Security
As the Arctic’s geopolitical significance grows, NATO must remain proactive in addressing emerging security challenges. The region’s changing geography, new shipping routes, and abundant natural resources have made it increasingly important for global stability. NATO’s strategic priorities for Arctic security focus on maintaining peace, enhancing military readiness, and fostering cooperation with Arctic nations.
- Strengthening Partnerships with Non-NATO Arctic Nations
NATO has long worked with non-NATO Arctic nations, including Sweden, Finland, and Canada, to address regional security concerns. While NATO does not directly engage in territorial disputes, it fosters cooperation through joint exercises, search and rescue operations, and environmental protection initiatives. NATO’s partnership with Finland and Sweden became even more significant as Finland joined NATO in 2023. Engaging these nations helps reduce tensions and supports a collective security framework in the Arctic. - Investing in Arctic-Specific Capabilities
NATO has focused on developing specialized capabilities for Arctic operations. This includes investments in ice-capable vessels, advanced surveillance technologies, and training to operate in extreme conditions. The alliance’s Arctic capabilities are regularly tested in joint military exercises such as "Trident Juncture," which includes scenarios specific to Arctic warfare. NATO also continues to prioritize technological innovation to maintain effective communication, navigation, and security in this challenging environment. - Enhancing Military Readiness
NATO’s military presence in the Arctic has been a cornerstone of its strategy in the region. The alliance conducts regular exercises, such as "Cold Response," involving thousands of troops from member states, to ensure operational readiness in Arctic conditions. The establishment of the NATO Joint Force Command Norfolk and the NATO Response Force allows for rapid deployment in response to emerging threats in the High North. These efforts enhance interoperability and ensure NATO can safeguard its interests in the region. - Ensuring Secure and Sustainable Arctic Shipping
With new shipping routes such as the Northern Sea Route and Northwest Passage becoming more navigable, NATO plays a critical role in maintaining security and stability along these routes. The alliance supports the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and promotes the free and secure passage of ships through international waters. NATO’s focus on maritime security, including protecting infrastructure like energy pipelines and shipping lanes, ensures that Arctic trade remains safe from geopolitical tensions and piracy. - Addressing Environmental and Climate Security
Climate change is transforming the Arctic, with shrinking ice cover opening new trade routes and exposing natural resources. NATO has recognized the intersection of climate and security, particularly how environmental changes impact military operations. NATO supports initiatives such as the Arctic Council's focus on sustainable development and environmental protection, while also addressing the security implications of environmental changes, such as extreme weather events or shifting territorial claims.
By addressing these priorities, NATO ensures that it remains a key player in the Arctic’s evolving security landscape. Through cooperation with Arctic nations, investment in specialized capabilities, and a focus on maintaining stability in the region, NATO will continue to contribute to the security of the High North and global trade routes.
Conclusion
The Arctic has evolved from a remote frontier into a critical region at the center of global geopolitics. NATO's increasing involvement in securing Arctic shipping lanes underscores its commitment to maintaining peace and stability in this strategically important area. NATO's expanded surveillance operations and joint military exercises, such as "Cold Response," have enhanced the alliance's readiness to address emerging threats. Additionally, NATO's partnerships with Arctic nations have strengthened intelligence sharing and strategic coordination among member states.
By addressing geopolitical rivalries and cybersecurity challenges, NATO is positioning itself as a key actor in managing the complexities of the Arctic. However, non-NATO perspectives, including those advocating for collaborative governance through bodies like the Arctic Council, are also crucial for ensuring regional stability and sustainable resource management.
As the alliance continues to adapt to the evolving Arctic landscape, its actions will have significant implications for both global security and economic prosperity. For policymakers, businesses, and citizens, understanding NATO's role in the Arctic is essential for navigating the region's growing challenges and opportunities.







