What Is NGAD? U.S. Air Force’s 6th-Gen Fighter Explained | AI, Drones, Stealth
Discover everything about NGAD—the U.S. Air Force’s sixth-generation air dominance program. Learn how AI, stealth, and unmanned systems redefine the future of air combat.

What Is NGAD? A Complete Guide to the Next Generation Air Dominance Program
Keyword focus: Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD), sixth-generation fighter jet, U.S. Air Force NGAD, future of air combat, Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA), Next Generation Aerial Refueling System (NGAS), AI in air warfare.
Introduction: What Is NGAD and Why It Matters
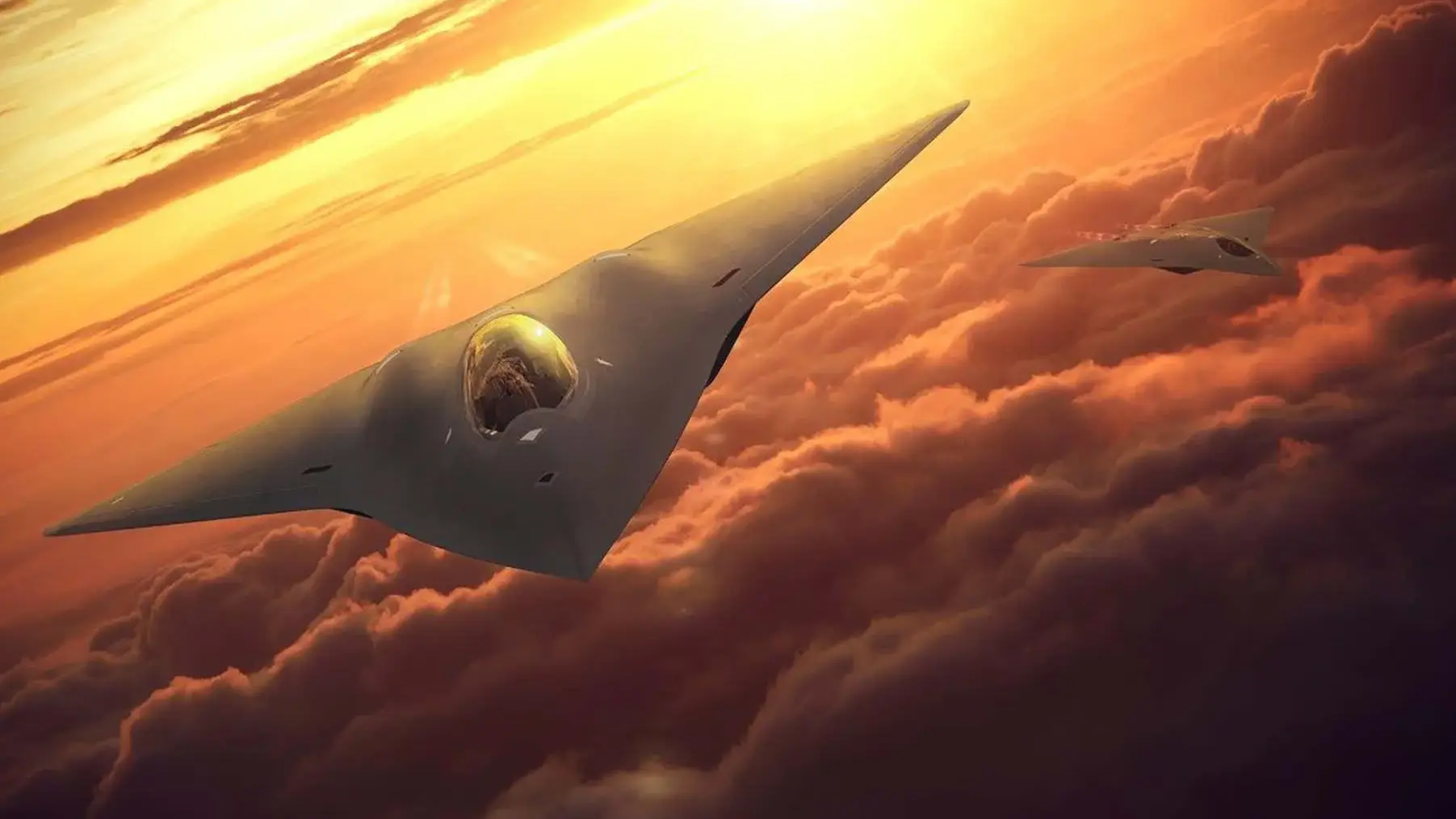
The Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program is the U.S. Air Force’s most advanced air combat initiative, created to ensure air superiority in the face of rising global threats. Set to replace the F-22 Raptor, NGAD is a sixth-generation fighter platform that integrates stealth, AI, autonomous systems, and long-range strike capabilities to counter near-peer adversaries like China and Russia.
NGAD is more than just a fighter jet—it's a system of systems, designed to operate in tandem with unmanned drones (CCA), stealth refueling tankers (NGAS), and advanced AI-driven combat tools.
Key Features of the NGAD Fighter Jet
NGAD marks a major evolution in U.S. airpower. Here are the core technologies defining this sixth-generation platform:
Stealth Manned Fighters
- Enhanced radar evasion
- Extended combat range
- Built for survivability in contested airspace
Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA)
- AI-powered unmanned drones
- Perform reconnaissance, electronic warfare, and strike missions
- Operate alongside piloted aircraft as loyal wingmen
Advanced AI and Autonomy
- Reduced pilot workload via AI copilots
- Real-time decision support and mission planning
- AI-piloted aircraft like the VISTA F-16
Next-Gen Sensors and Networking
- Seamless multi-platform data sharing
- Real-time battlefield awareness
- Integration across domains (air, cyber, space)
Adaptive Propulsion
- Next-generation jet engines
- Greater fuel efficiency and mission endurance
Why NGAD Is Critical for U.S. Military Strategy
Deterring Threats in the Indo-Pacific
NGAD fills operational gaps in the Pacific theater, especially over long distances where stealth, fuel range, and AI coordination are vital.
Countering Fifth-Gen Fighters & SAMs
With near-peer adversaries deploying hypersonic weapons and anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) systems, NGAD ensures the U.S. stays ahead of evolving threats.
NGAD vs. F-35 Lightning II: Key Differences
| Feature | F-35 Lightning II | NGAD |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | 5th | 6th |
| Role | Multi-role (strike & recon) | Air Superiority |
| Stealth | High | Next-Level Stealth |
| Unit Cost | ~$80 million | ~$300 million |
| Combat Range | Moderate | Extended for Indo-Pacific |
| AI Integration | Moderate | Advanced |
Verdict: The NGAD platform is purpose-built for dominance in future high-end conflicts, going far beyond the multi-role versatility of the F-35.
Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA): The AI Wingman
The CCA program introduces autonomous drones that support human pilots in real-time operations. This enables NGAD aircraft to offload high-risk tasks to unmanned platforms.
Key Capabilities:
- Surveillance and Recon: Expand threat detection range
- Electronic Warfare: Jam or disable enemy sensors
- Strike Support: Launch weapons while piloted jets remain at standoff distances
Next Generation Aerial Refueling System (NGAS)
To sustain global operations, the NGAS introduces stealth refueling tankers that can survive in contested areas.
Benefits:
- Low Observability: Operate closer to frontlines
- Fuel Efficiency: Support long-range missions in the Pacific
- Autonomous Compatibility: Refuels both manned and unmanned aircraft
AI in NGAD: Transforming Air Warfare
Artificial intelligence is central to NGAD’s mission success. From autonomous flight to predictive maintenance, AI is woven into every layer.
Real-World AI Use Cases:
- Vista AI F-16: Successfully completed complex aerial maneuvers without a human pilot
- AI in Combat: Real-time threat recognition, targeting, and evasion
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduces aircraft downtime and increases readiness
Challenges: Cost and Development Risks
At $300 million per unit, NGAD is among the most expensive fighter platforms ever built. Combined with the F-35’s $2 trillion lifecycle cost, budget allocation remains a concern.
Solutions in Progress:
- Partnering with private industry to reduce R&D expenses
- Prioritizing essential capabilities over quantity
- Pushing for expanded defense budgets amid growing threats
Strategic Impact: Preparing for Near-Peer Conflict
NGAD plays a critical role in deterring near-peer adversaries, particularly in light of potential flashpoints like Taiwan.
U.S. Focus Areas:
- Power Projection in the Indo-Pacific
- Disrupting the Enemy Kill Chain
- Fortifying U.S. Base Defenses against missile and drone strikes
Conclusion: The Future of Air Dominance Is Here
The Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program is more than just a replacement for the F-22—it's a revolutionary leap in military aviation. By integrating stealth, AI, drones, and next-gen weapons, NGAD ensures the U.S. maintains control over future contested skies.
As Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall said:
“There comes a point where you simply need more resources to accomplish more missions.”
The future of air warfare will be fought—and won—by NGAD.

FAQs: Everything You Need to Know About NGAD
When will NGAD be operational?
Initial Operational Capability (IOC) is expected by 2030.
What makes NGAD a sixth-generation fighter?
It includes advanced stealth, AI integration, hypersonic weapons, and collaborative drone systems.
How much does NGAD cost?
Each NGAD unit is projected at ~$300 million, making it one of the most advanced and expensive fighters ever.
Read more stories on Air Combat & Aviation here on Großwald:

Related Topics
- France’s Dassault Rafale F4 and F5: Next-Gen Connectivity, Drone Ops, and Strike Precision
- USAF Boeing KC-46A Pegasus Tankers Struggle with Readiness
- AI-Generated Infrared Images for Military Targets
- DARPA Bets $12M on BAE Systems FAST Labs High-Temp Sensors
- Inside the Blue UAS Program: The Pentagon’s Top Drones in 2025






